EtherCAT in industry

EtherCAT (Ethernet for Control Automation Technology) is an industrial network standard developed by Beckhoff (Germany) in 2003. It is one of the fastest data transfer protocols. Typical cycle time of EtherCAT is 50 to 250 µs. EtherCAT belongs to the Industrial Ethernet family and is used for distributed real-time control.
EtherCAT specifics
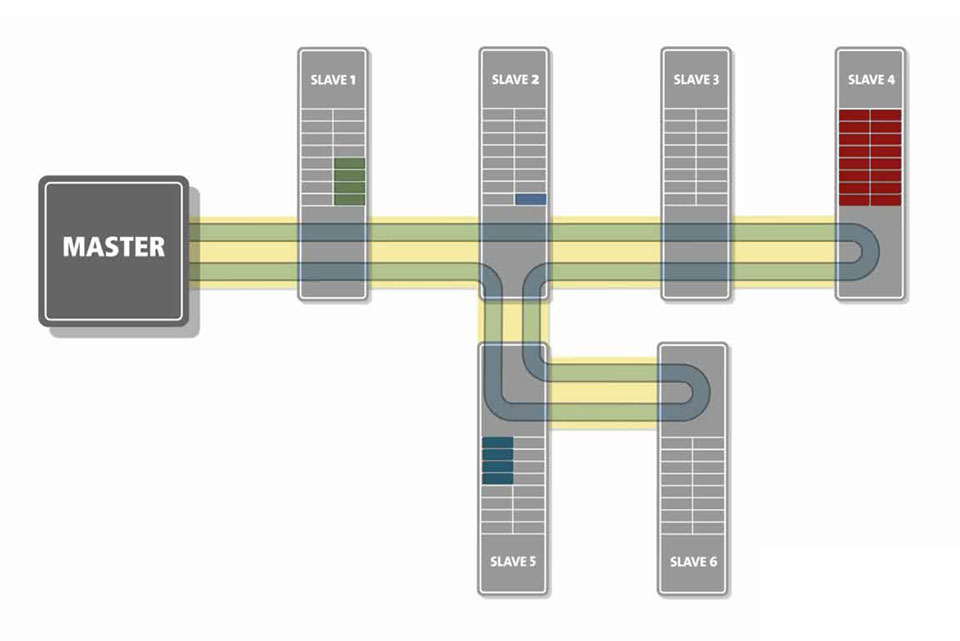
Compared to a usual Ethernet challenge-response concept, where a device on the network receives a data packet, processes it, and sends a response, EtherCAT technology uses a different approach called on-the-fly processing. How it works:
- A master sends a datagram (data packet) to slaves connected to the network
- a device reads the packet header, recognizes the EtherCAT packet, and immediately starts processing it
- "on-the-fly" receives and replaces the necessary bits, sending a packet to the next network element
- so the datagram passes sequentially through all devices on the network and returns to the master
This approach achieves cycle time in the microsecond range. That is one of the highest rates among other industrial Ethernet solutions.
Benefits of EtherCAT technology
- Real-time Ethernet protocol at all layers with high performance
- Full compatibility with standard Ethernet network equipment
- Efficient use of Ethernet bandwidth
- Flexible topology
- Low system implementation costs
- Compatibility with valid industrial buses
Industrial implementation of EtherCAT
There are fields in the industry, where it is critical to achieve cycle time of less than 1 ms. For example, fast processes in power engineering - control and regulation of electrical quantities: current, voltage, power, frequency, and phase. It is also important to ensure the registration speed of emergency situations and technological protection at generating stations or high-voltage inverter installations.
Another example of fast processes is multi-axis motion control in CNC systems with high cutting speed and high demands on positioning accuracy and synchronization. There is the following selection of EtherCAT applications:
- robotics, metalworking or metal molding, machine tools, instrumentation
- control of physical processes, as well as their regulation with ensuring high data security
- organization of the operation of measuring systems where high accuracy, synchronism, and the use of several channels of data transmission and processing are required